Site Directed Mutagenesis.
The nucleotide sequence of DNA encodes various types of information used by the cell, including the amino acid sequence of all the proteins found in Nature. Therefore, changing the sequence of nucleotides in DNA may result in alterations in the amino acid sequences of proteins. The process of changing the nucleotide sequence of DNA is called mutagenesis, and the altered sequence is referred to as mutant DNA. The process of mutation of DNA is closely monitored and rapidly corrected by the cell, and so mutations are relatively rare events. However, although mutation is rare, over long periods of time it is inevitable that mutations will accumulate in a given DNA sequence.

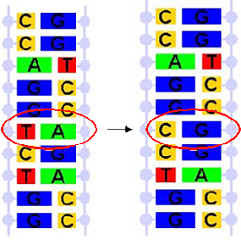
Using modern techniques of molecular biology, specific mutations may be introduced into any DNA sequence, and any particular nucleotide in a DNA sequence may be substituted by any other. This powerful technique is called site directed mutagenesis, and is a common tool that is used for the manipulation of amino acid sequences of proteins.